What are the molecular targeted drugs for cancers with BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations?
BRCA1およびBRCA2遺伝子変異を持つがんに対する分子標的薬で注目されているのはPARP阻害剤(PARPi)です。現在、FDAに承認されているPARPiは4種類あり、これらはBRCA1/2欠損がんの治療に利用されています(Ragupathi et al., 2023)。
最初に承認されたPARPiであるオラパリブは、BRCA変異を持つ卵巣がん患者の治療において非常に有望な結果を示しています(Venkitaraman, 2009; Tangutoori et al., 2015)。PARPiは、がん細胞のゲノム不安定性を利用してDNA損傷応答を標的とし、従来の化学療法と比較してより腫瘍細胞選択的なアプローチを提供します(O’Connor, 2015)。
PARPiの細胞毒性は、BRCA1/2変異腫瘍の複製が困難なゲノム領域に過剰な複製ストレスを誘導することによると考えられています(Ragupathi et al., 2023)。現在進行中の研究では、PARPiと免疫チェックポイント阻害薬を組み合わせて臨床結果を向上させる方法が探求されています(Ragupathi et al., 2023)。さらに、PARPiは他のさまざまながんタイプに対しても、単独療法および他の治療法との併用療法としての利用が検討されています(Tangutoori et al., 2015)。
このように、PARP阻害剤はBRCA1/2遺伝子変異を持つがん患者にとって新たな希望となる治療法であり、今後の研究と臨床応用が期待されています。
Molecular targeted drugs for cancers with BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations primarily focus on PARP inhibitors (PARPi). Four FDA-approved PARPi are currently available for treating BRCA1/2-deficient cancers (Ragupathi et al., 2023). Olaparib, the first approved PARPi, has shown promise in treating ovarian cancer patients with BRCA mutations (Venkitaraman, 2009; Tangutoori et al., 2015). PARPi exploit the genomic instability of cancer cells by targeting the DNA damage response, offering a more selective approach compared to traditional chemotherapy (O’Connor, 2015). The cytotoxic effect of PARPi is believed to result from inducing excessive replication stress in difficult-to-replicate genomic regions of BRCA1/2 mutated tumors (Ragupathi et al., 2023). Ongoing research explores combining PARPi with immuno-oncology drugs to enhance clinical outcomes (Ragupathi et al., 2023). Additionally, PARPi are being investigated for use in various other cancer types, both as monotherapies and in combination with other treatments (Tangutoori et al., 2015).
References
O’Connor, M. J. (2015). Targeting the DNA Damage Response in Cancer. 60(4), 547–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.040
Ragupathi, A., Singh, M., Perez, A. M., & Zhang, D. (2023). Targeting the BRCA1/2 deficient cancer with PARP inhibitors: Clinical outcomes and mechanistic insights. 11, 1133472. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2023.1133472
Tangutoori, S., Baldwin, P., & Sridhar, S. (2015). PARP inhibitors: A new era of targeted therapy. 81(1), 5–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2015.01.015
Venkitaraman, A. R. (2009). Targeting the molecular defect in BRCA-deficient tumors for cancer therapy. 16(2), 89–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.07.011
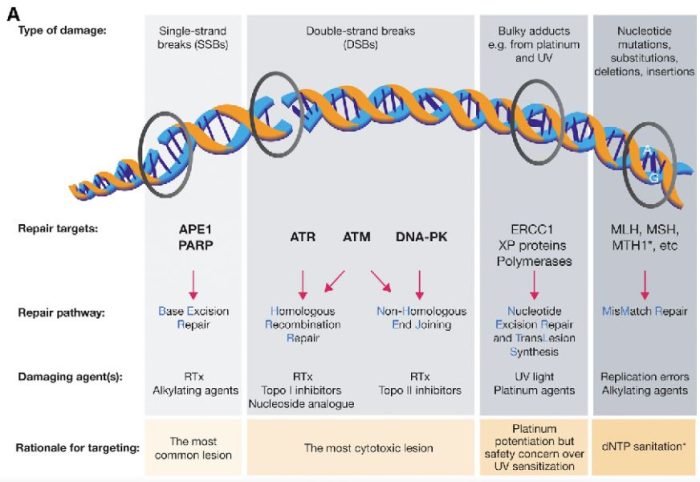
図の解説:PARP(ポリ(ADP-リボース)ポリメラーゼ)は、主に一重鎖DNA切断(single-strand breaks, SSB)の修復に関与しています。具体的には、以下のようなDNAダメージを修復します:
- 一重鎖切断(SSB): DNAの片方の鎖が切断される損傷です。PARPはこの損傷を検出し、修復プロセスを開始します。
- 塩基除去修復(BER): DNAの塩基が損傷を受けた場合、PARPはこの修復経路に関与し、損傷した塩基を除去し、新しい塩基を挿入するプロセスを助けます。
PARPは、これらの損傷を修復することで、細胞のゲノム安定性を維持し、細胞の生存を助けます。しかし、BRCA1やBRCA2遺伝子に変異がある場合、これらの修復経路が正常に機能しないため、PARP阻害剤(PARPi)はこれらのがん細胞に対して特に効果的です。PARPiはPARPの機能を阻害することで、がん細胞に蓄積するDNA損傷を増加させ、最終的にがん細胞の死を誘導します。
PARP分子と、Olaparibの結合を結晶構造で眺めてみました。この構造だと、PARPたんぱく質に結合したOlaparibは分子の中に深く埋もれているように見えます。(結合した後にたんぱく質の構造変化が起きる?)緑色の分子がolaparibで、それ以外が human PARPのcatalytic domain。下図は下記文献のデータを基にわたくしが作図しました。
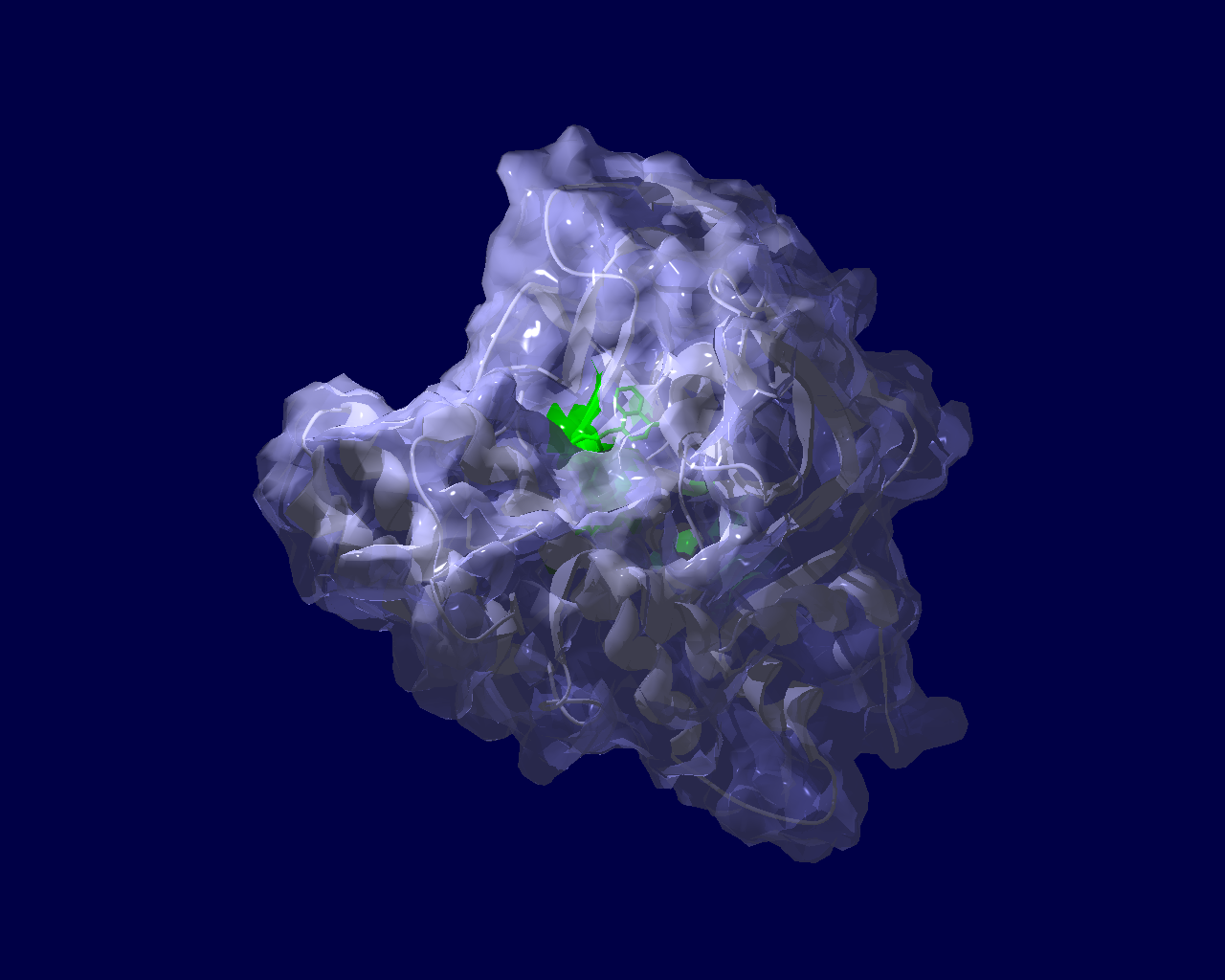
Ogden, T. E. H., Yang, J.-C., Schimpl, M., Easton, L. E., Underwood, E., Rawlins, P. B., McCauley, M. M., Langelier, M.-F., Pascal, J. M., Embrey, K. J., & Neuhaus, D. (2021). Dynamics of the HD regulatory subdomain of PARP-1; substrate access and allostery in PARP activation and inhibition. 49(4), 2266–2288.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab020

