頭蓋咽頭腫の病理 craniopharyngioma
craniopharyngioma WHO grade 1
- 頭蓋咽頭腫には,5-15歳(小児)のピークと45-60歳(成人)のピークの2つの好発年齢層があります。乳児を含めて全ての年齢で見られます。原発性脳腫瘍の0.5-2.5%と珍しい腫瘍と言えますが,14歳以下の小児では5-10%を占め小児脳腫瘍としては多い部類の疾患です。
- 発生母地は,隆起部 pars tuberalisのRathke pouchと呼ばれる類上皮の憩室といわれています。部位は神経下垂体 neurohypophysisであり,第3脳室底(視床下部灰白隆起 tuber cinereum),下垂体柄 (pituitary stalk),下垂体中間葉後葉 (pars intermedialis, posterior lobe)の起源のいずれかとなります。臨床的にも,この発生部位によって腫瘍の存在部位と伸展方向が異なります。
- 病理学的には,adamantinomatous type と papillary typeの2つに分類されますが,papillary typeは成人にしか発生しません。従って,adamantinomatous typeが圧倒的に多いといえます。adamantinomatous typeはneoplastic transformation of primitive craniopharyngeal duct remnantから,papillary typeはanterior pituitary cell metaplasiaという意見もありますが,確定していません。この説では,papillary typeが第3脳室に多いということを説明できないです。
- papillary typeはBRAF mutation,adamantinomatous typeはCTNNB1 mutationが原因遺伝子とされています。
臨床的に大切なこと
頭蓋咽頭腫は境界明瞭な良性腫瘍として知られていますが,病理学的にはそうではありません。頭蓋咽頭腫は周囲の正常組織に食い込むように潜り込んで増殖します。例えば,視床下部脳組織に浸潤ではなくて侵入し癒着しています。それを視床下部から剥離して完全に摘出しようとすれば,視床下部損傷は避け得ません。
adamantinomatous type(ほとんどこのタイプ)
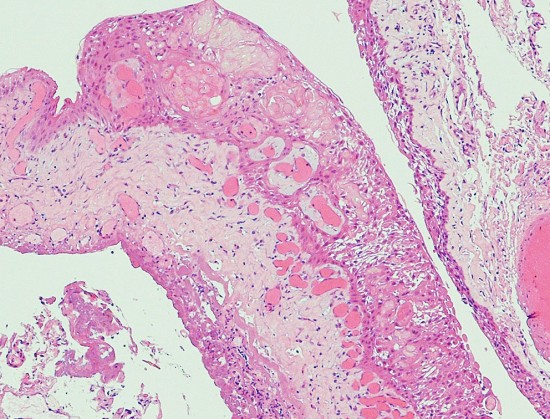
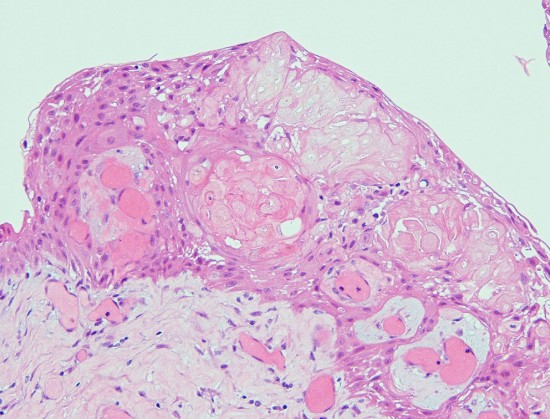
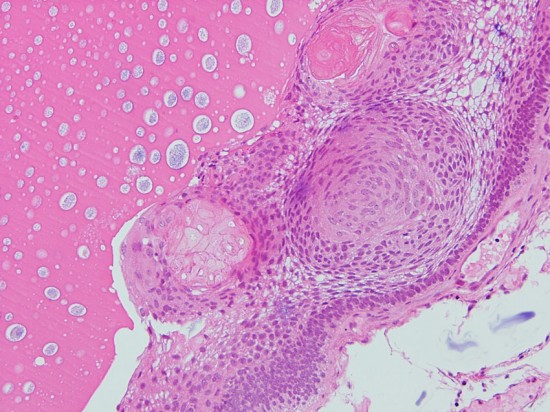
エナメル上皮腫型といいます。組織学的にはwet keratinを含むことが特徴で,この所見でpapillary typeと区別ができます。基底層が一列に配列し,それに続いて上皮細胞があり,一部に疎な結合職と小血管の部分,石灰化,小のう胞が存在します。のう胞内容液は,肉眼的に暗緑褐色でmachinery oilと表現される。脳組織(特に視床下部)に浸潤し,神経や血管に癒着します。まれに石灰化ではなく,真の骨化がみられる。
adanmantinomatous type 主要所見 (by Dr. 継仁)
- palisaded columnar epithelium
- stellate reticulum cells
- wet keratin / carcification
- whorl formation
- cystic degeneration
- xanthogranulomatous change
Scarce squamous epithelium with basal vascular network of cyst wall
“Wet keratin” in an epithelial layer.
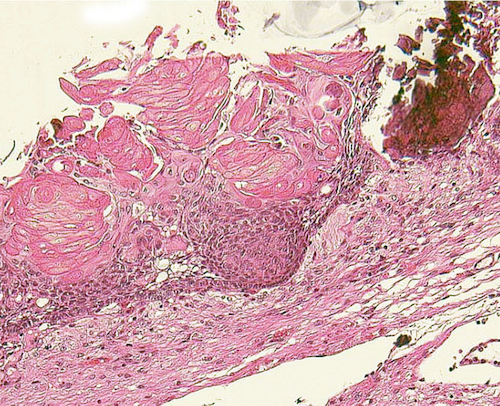
Craniopharyngioma with wet keratin structures (upper left) and calcification (upper right).
Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma showing well-differenciated squamous epithelium including whorl of squamous cells. MIB-1 index of the dense basal layer was approximately 10%.
Xanthogranulomatous part in an adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma showing cholesterol clefts (upper left) surrounded by collagen tissue, dense macrophage infiltration, and lymphatic infiltrates (upper right)
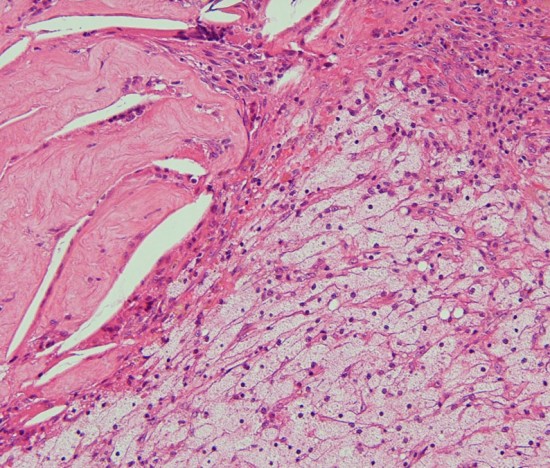
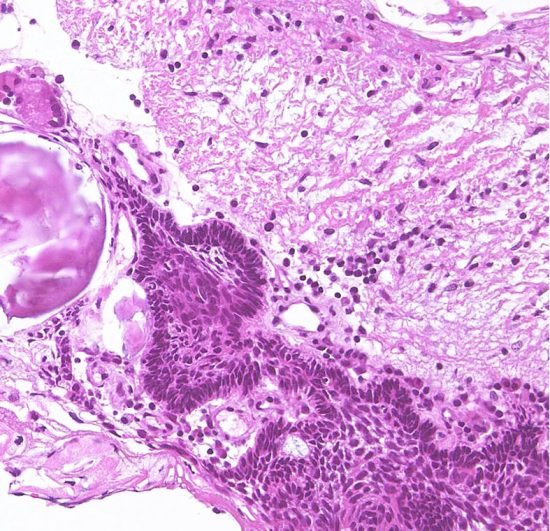
視床下部浸潤(よくあることで重要)
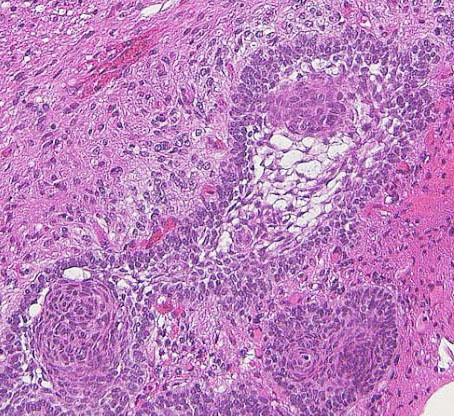
Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma invading brain tissue. This type of hypothalamic invasion is frequently seen in the suprasellar/ intraventricular craniopharyngioma.
The border between tumor cells forming lateral palisading (center) and hypothalamic glial tissue (upper right) is not clear. There is no cleavage plane.
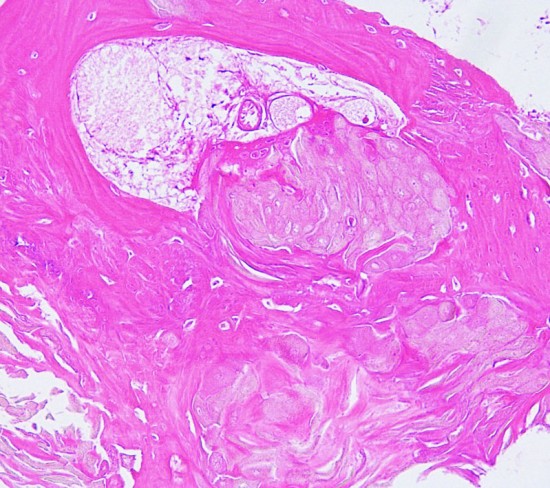
adamantinomatous typeのfinger-like protrusion
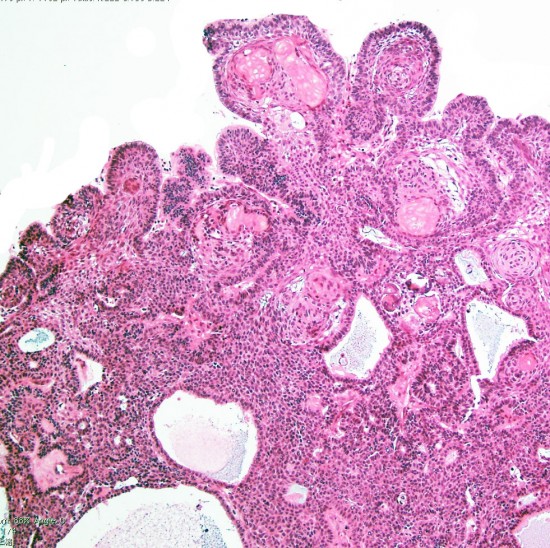
Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma showing surface finger (tongue)-like protrusion contains small cysts, wet keratin, and stellate reticulum.
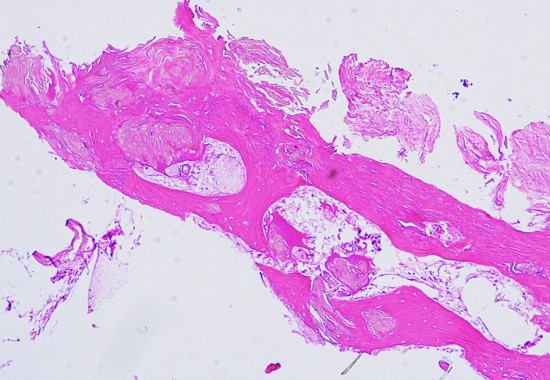
骨化 ossification (まれだけど大切な所見)
A large piece of mature bone in a suprasellar craniopharyngioma.
文献
- Brastianos PK, et al.: Exome sequencing identifies BRAF mutations in papillary craniopharyngiomas. Nat Genet 46: 161-165, 2014
- Sekine S, et al.: Craniopharyngiomas of adamantinomatous type harbar beta-catenin gene mutations. Am J Pathol 161: 197-2001,, 2002
- Buslei R, et al.: Common mutations of beta-catenin in adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma but not in other tumors originating from the seller region. Acta Neuropathol 109: 589-597, 2005
- 継仁, et al.: 脳神経外科医のための,頭蓋咽頭腫の病理から見た臨床, 脳神経外科速報, 2009