What are CDC42 and Takenouchi-Kosaki syndrome?
Takenouchi-Kosaki syndrome is a congenital malformation syndrome characterized by macrothrombocytopenia, intellectual disability, characteristic facial features, sensorineural deafness, brain structural abnormalities, contracture of the fingers, lymphedema, repetitive infections, and hypothyroidism. Although many symptoms are present, this condition can be diagnosed clinically based on a combination of symptoms. This condition is caused by an abnormality in a gene called CDC42. On the other hand, not everyone with mutations in the CDC42 gene will have the same symptoms; only those with a mutation in a specific part of the CDC42 gene appear to exhibit the characteristic symptoms described above.
Prevalence
Cause
Inheritance
Differential diagnosis
Treatment
Symptoms
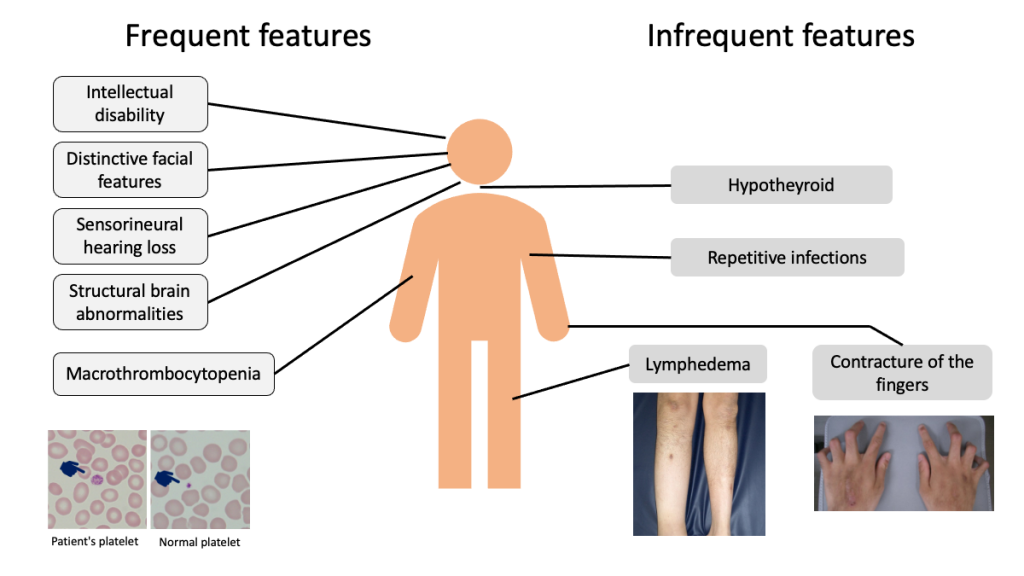
Macrothrombocytopenia
Blood test findings that are characteristic of the disease include a decrease in the number of platelets and an increase in the size of some platelets. This can be confirmed by peripheral blood counts and smear tests performed as part of routine clinical practice. This finding is very important in making a diagnosis. In general, a low platelet count can cause bleeding, but patients with this disease do not have bleeding tendency.
Intellectual disability
Patients with this condition exhibit intellectual disability of varying degrees. Regression (a gradual loss of ability to do what was previously possible) is not seen.
Distinctive facial features
The following facial features are common in patients with Takenouchi-Kosaki syndrome.
- Dark eyebrows and slight hypertrichosis throughout
- Inverted crescent-shaped eyelids
- A short distance between the nose and mouth
- Thin upper lip
- Small mouth
- Protruding lower jaw, relative to the upper jaw
- Small earlobes
Structural brain abnormalities
The CDC42 gene, which is the cause of this disease, is important for brain formation and is associated with findings such as ventricular enlargement and cerebellar hypoplasia. Among the patients observed to date, a susceptibility to epilepsy has not been reported.
Sensorineural hearing loss
Patients with Takenouchi-Kosaki syndrome have sensorineural hearing loss to the extent that a hearing aid is required immediately after birth. The hearing loss is thought to be caused by dysplasia of the inner ear.
Contracture of the fingers
Flexion of the fingers and toes is present.
Lymphedema
“Swelling” occurring mainly in the lower extremities may be present, particularly in adult patien
Repetitive infections
Some patients are susceptible to recurring bacterial infections. While the exact cause is unknown, poor immunity is thought to be involved.
Hypothyroidism
A blood test may reveal hypothyroidism.