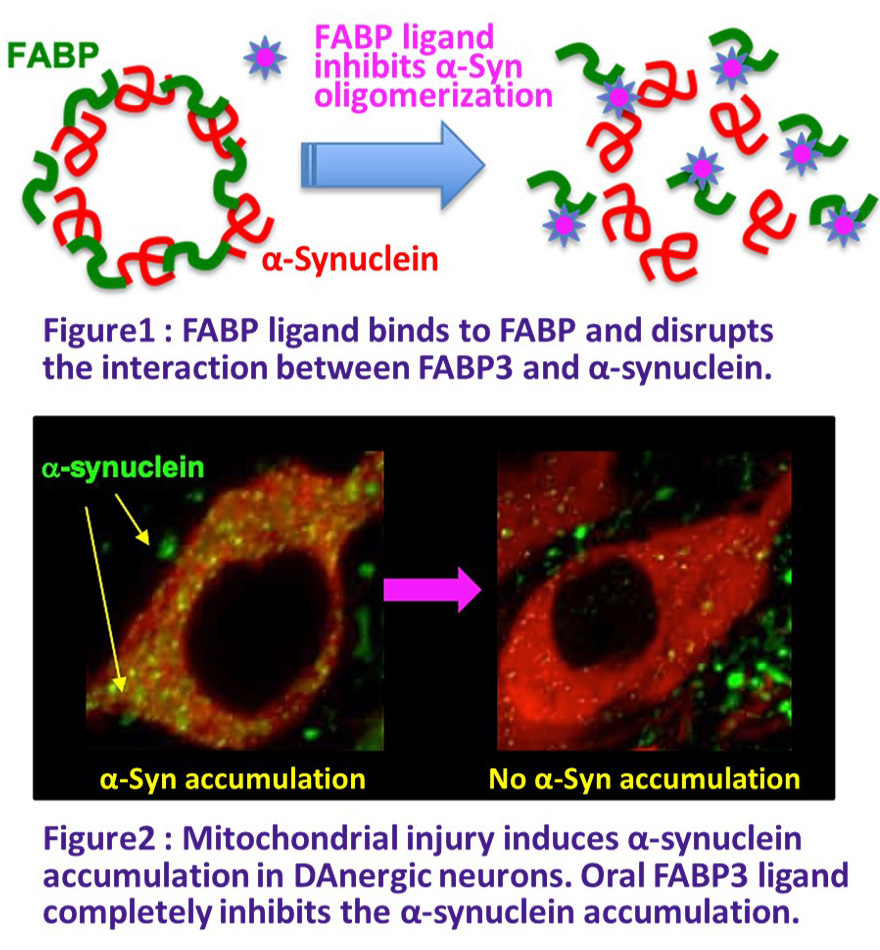
1.Development of a treatment for Lewy body disease that targets fatty acid-binding protein
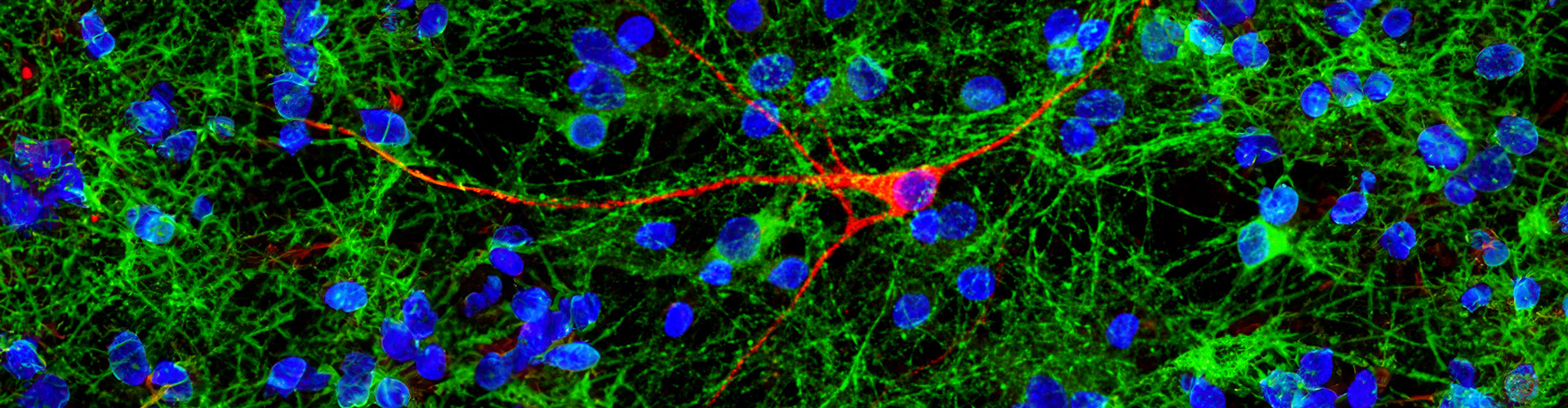
So far, we have succeeded in creating a number of lead compounds targeting fatty acid binding protein (FABP), and have succeeded in preventing the intracellular aggregation of α-synuclein, the causative protein of Lewy body disease. There are many types of FABP, and they are expressed in various cells, including glial cells and oligodendrocytes, as well as neurons. We are developing fundamental preventive and therapeutic drugs by creating these cell-specific ligands. The target diseases are Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson's disease dementia, and multiple system atrophy, and the FABP3 ligand (WO2017171053 A1) is scheduled to complete preclinical trials in 2025.
*2023 “Bridge Research Program” adopted projects (Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development - AMED)
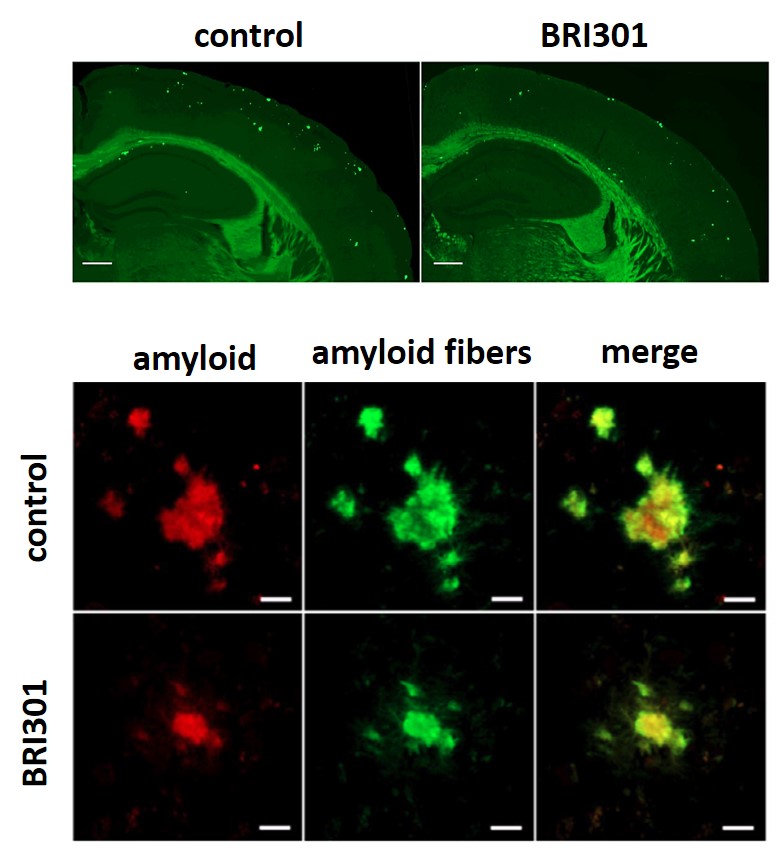
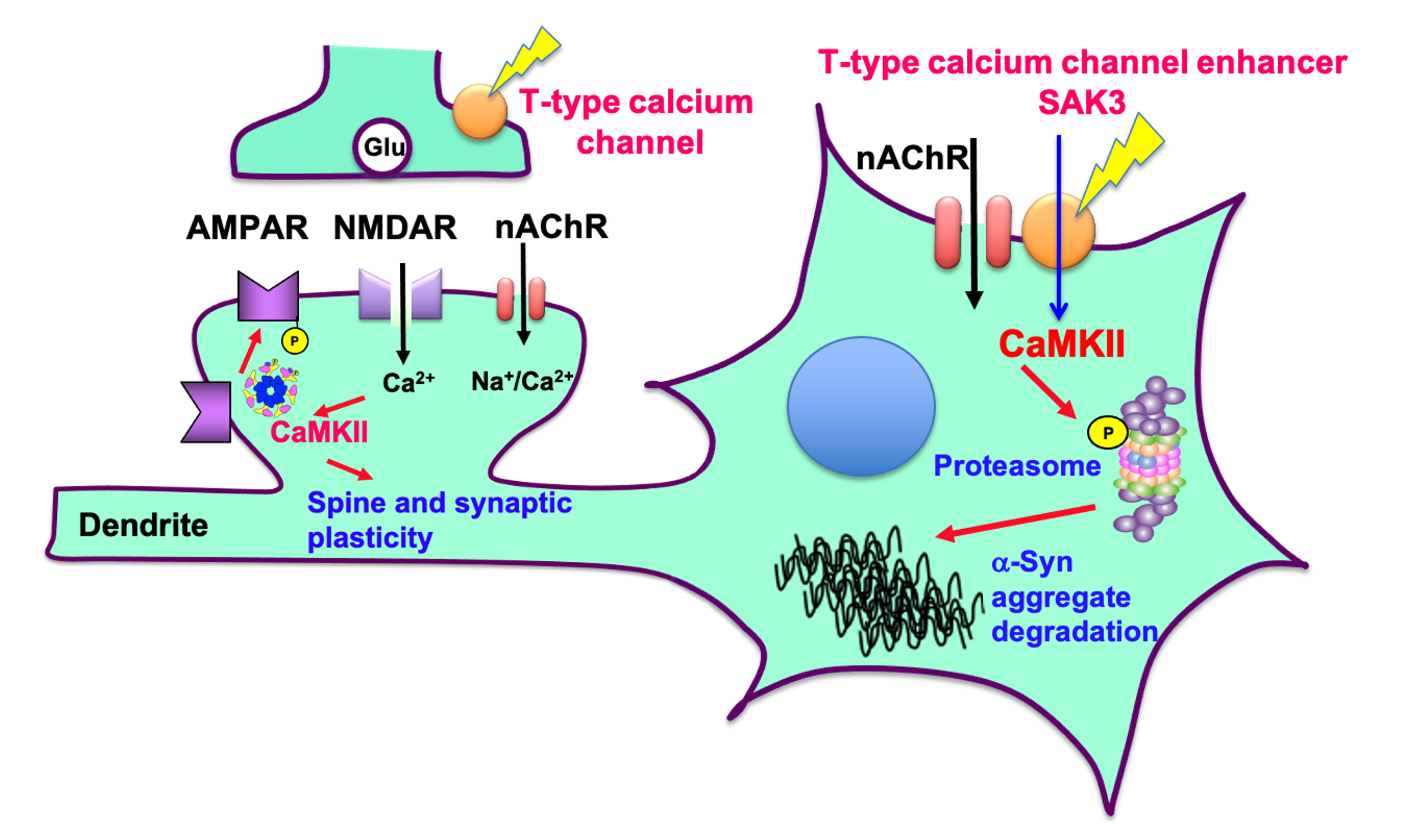
2.Development of a drug for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease that targets the proteasome
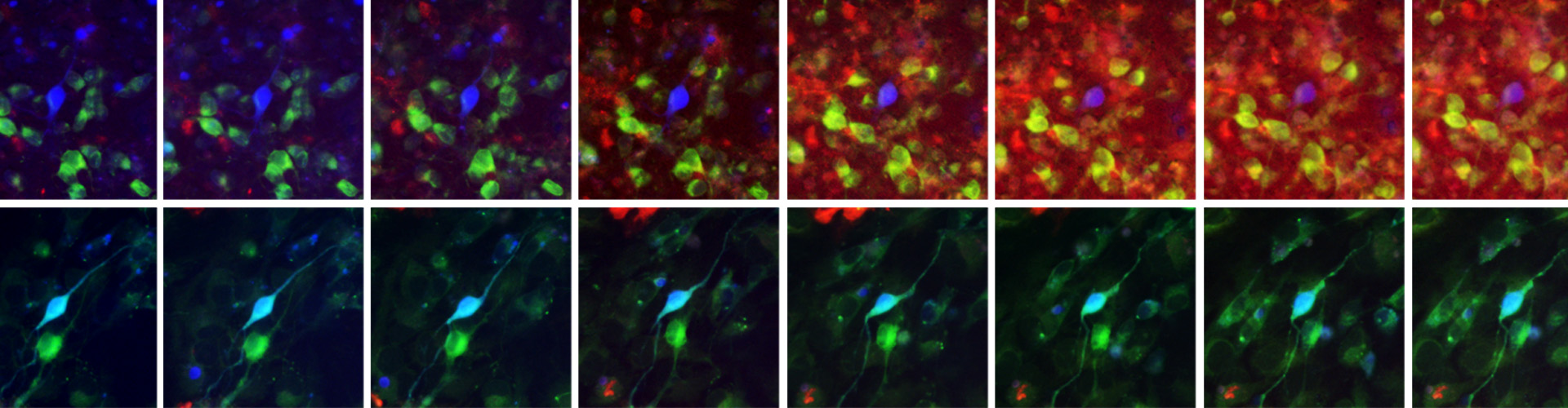
We have discovered a new method of removing denatured proteins in nerve cells by activating the proteasome, a device that breaks down denatured proteins. Furthermore, we have clarified the mechanism by which SAK3 activates the proteasome in nerve cells to promote the breakdown of denatured proteins. The results of this research are expected to be applied to the treatment of these diseases, as they promote the degradation of degenerative proteins such as amyloid-beta protein and tau protein, which are the causes of Alzheimer's disease, alpha-synuclein, which is the cause of Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies, and huntingtin, which accumulates in Huntington's disease, and prevent neuronal cell death.
*Tohoku University Press Release - http://www.pharm.tohoku.ac.jp/file/information/20210629.pdf
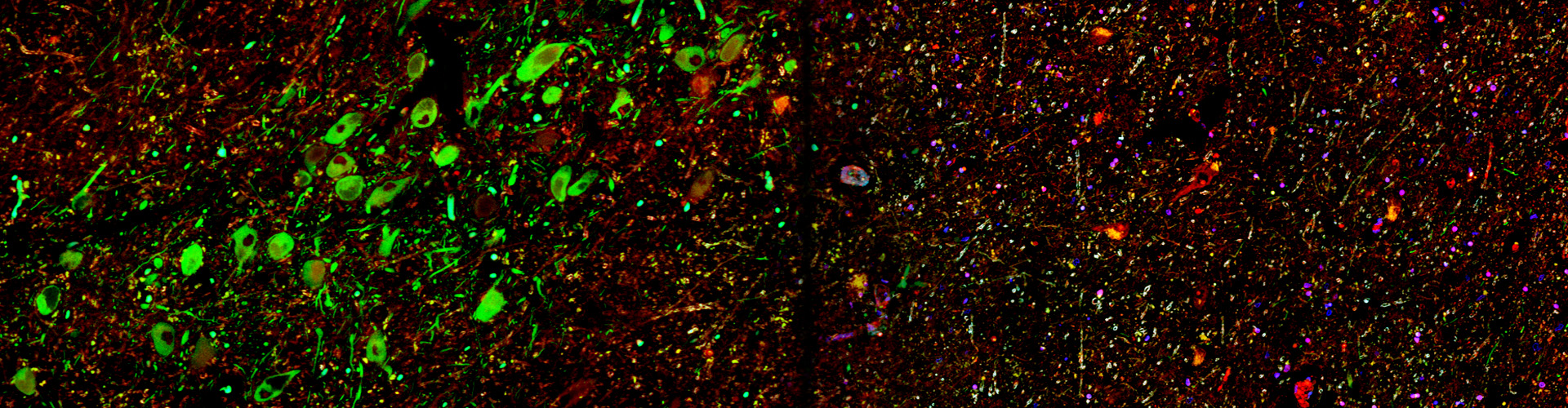
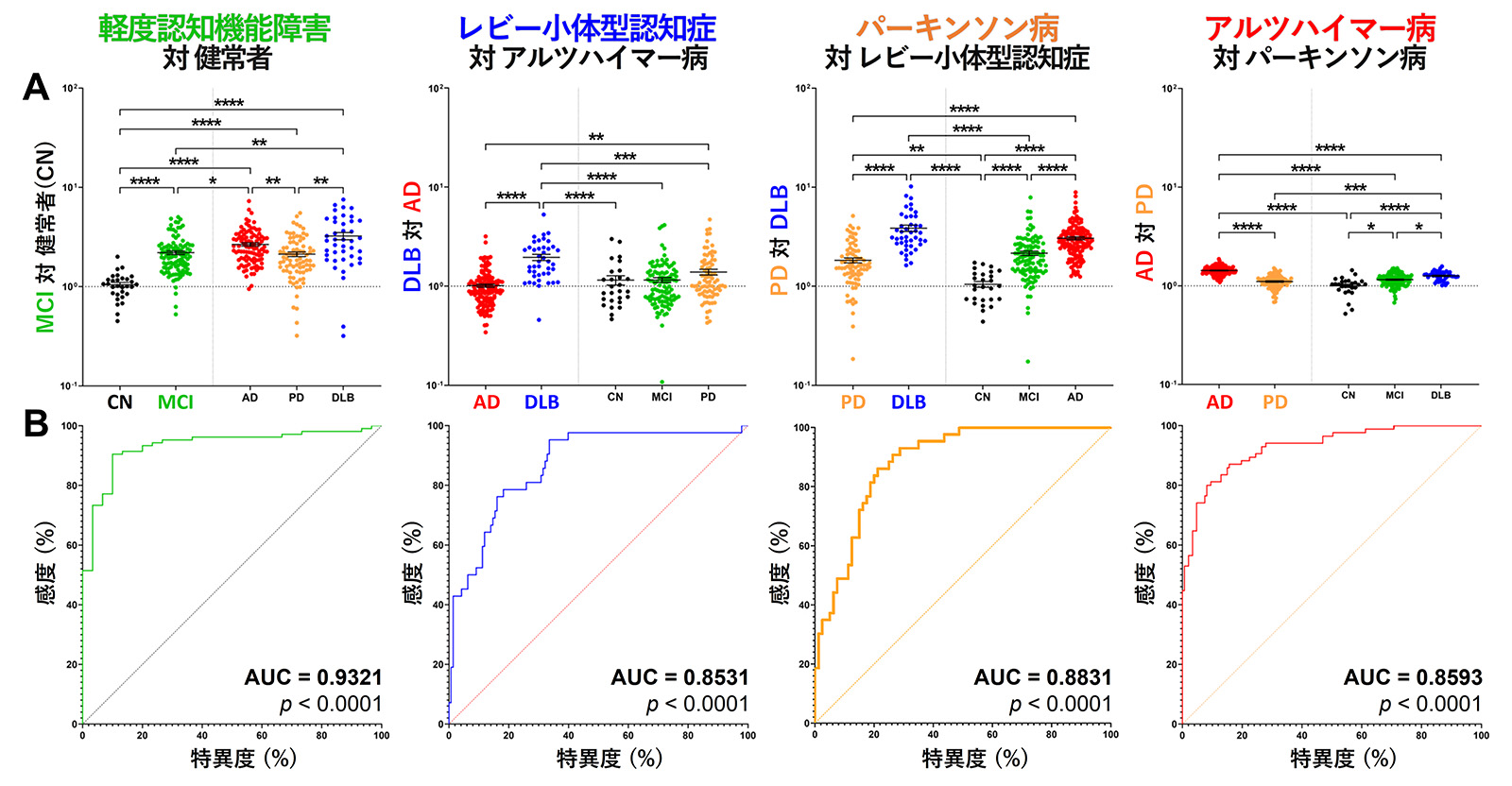
3.Development of ultra-early diagnostic technology for dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease
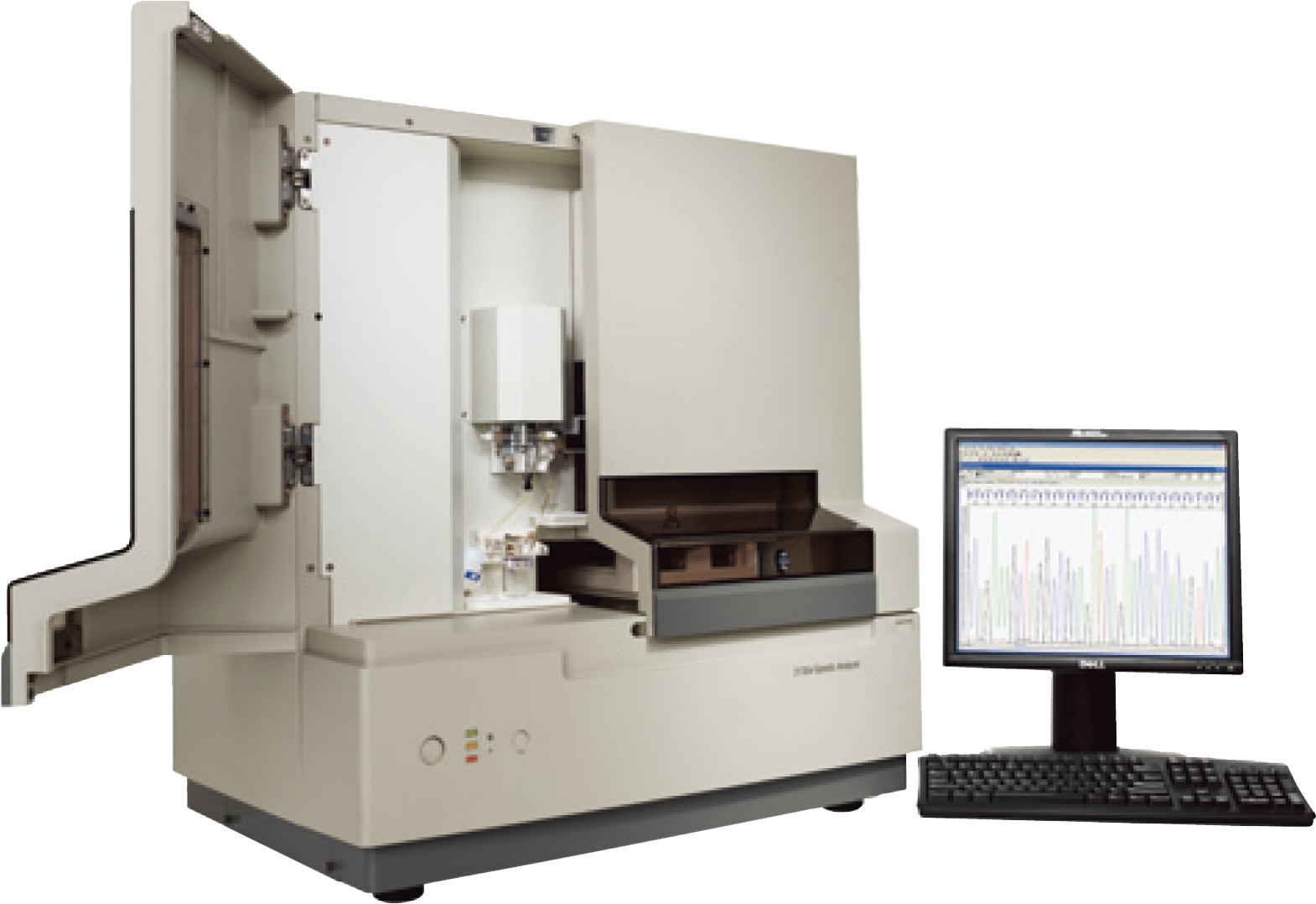
Recently, we have succeeded in developing a unique biomarker and quantification technology for Lewy body disease (patent application 2021-012620, WO2022163818 A1). This technology makes it possible to accurately distinguish between Lewy body dementia, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, and it is expected to be used for the diagnosis of cognitive and motor disorders before they develop. It is also possible to accurately screen patients for the above-mentioned therapeutic drugs, which will improve the accuracy of clinical trials and treatment effects.
Press Release: New Prediction and Differentiation Technology for Brain Diseases - Expectations for Ultra-Early Diagnosis of Dementia
→https://www.tohoku.ac.jp/japanese/2023/09/press20230925-03-ad.html
→http://www.pharm.tohoku.ac.jp/file/information/20230925.pdf
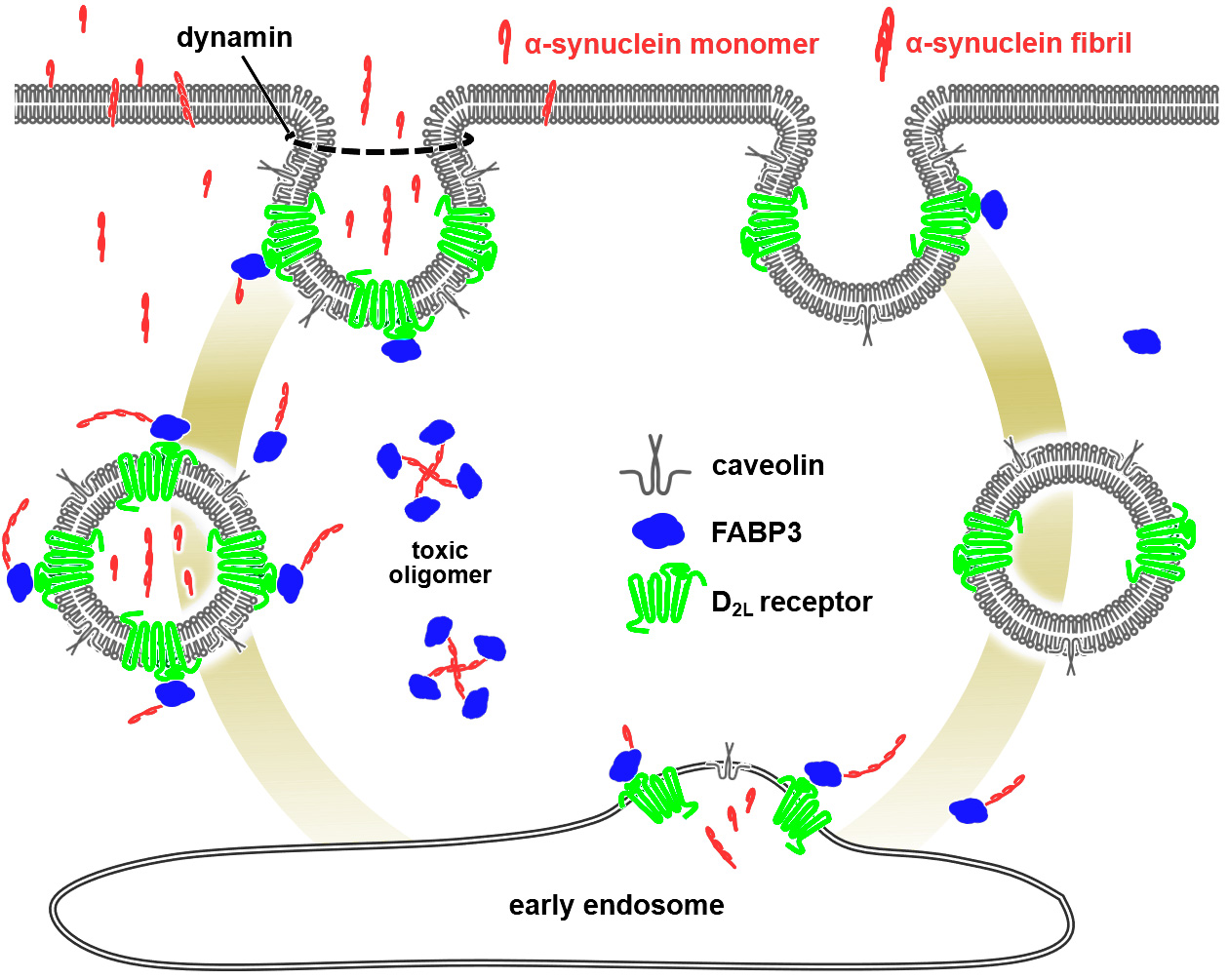
4.Elucidation of the pathogenic mechanism of Lewy body disease and the propagation mechanism of α-synuclein
Alpha-synuclein, the protein that causes Lewy body disease, is thought to cause the disease by spreading throughout the body and accumulating in the brain. We have discovered a new mechanism by which alpha-synuclein interacts with fatty acid binding protein FABP3 and various cell membrane surface receptors, and is taken into cells. We also found that this phenomenon leads to the loss of tyrosine hydroxylase, which is important for the biosynthesis of dopamine. We are also developing a treatment that can fundamentally inhibit the propagation of α-synuclein itself and prevent Lewy body disease (patent application 2020-127958, WO/2022/024693 A1).
*Kawahata I, Fukunaga K. Impact of fatty acid-binding proteins and dopamine receptors on α-synucleinopathy. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Feb;148(2):248-254. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2021.12.003. Epub 2021 Dec 14.
5.Genetic analysis of the causative genes of hereditary neurological and pediatric diseases and elucidation of the pathogenesis
We are conducting genetic analysis to deepen our understanding of neurology, with a focus on hereditary degenerative diseases, particularly pediatric hereditary diseases such as dopa-responsive dystonia (Segawa disease) and hereditary Parkinson's disease.