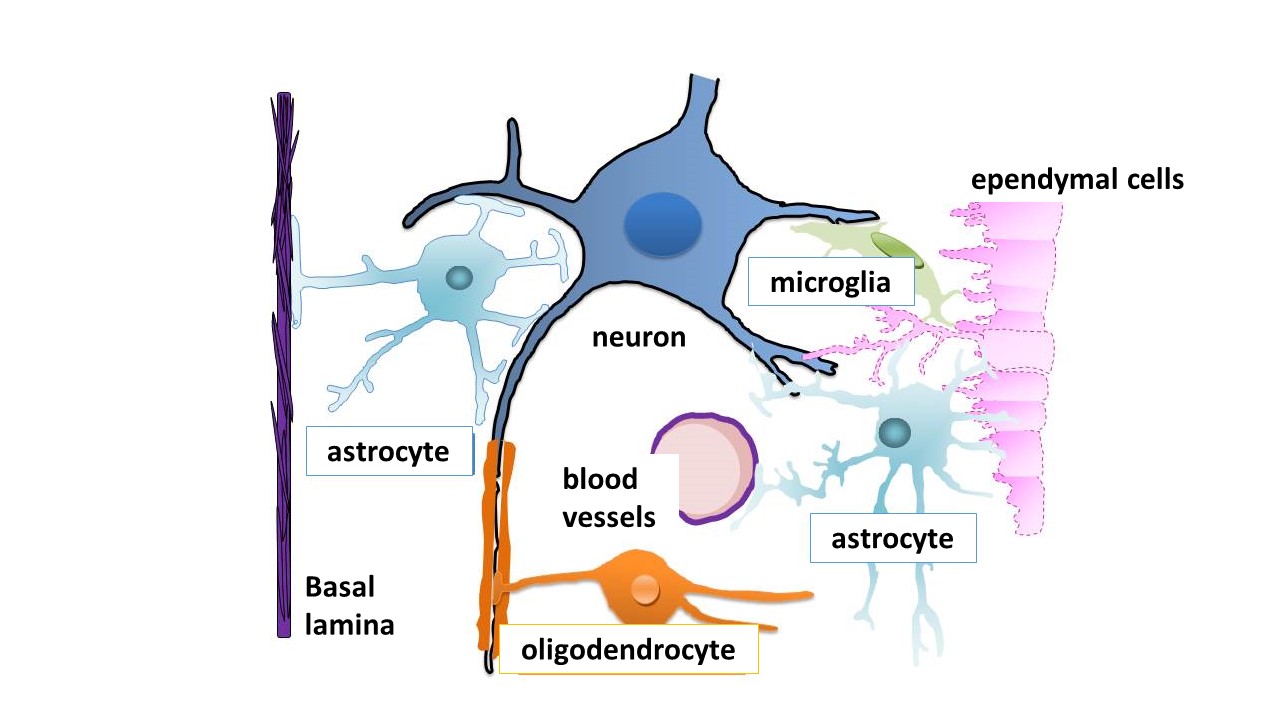
What is inherited white matter disorders?
Inherited disorders of the glial cells (Figure: right-hand side: oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and microglia), which account for the vast majority of cells in the central nervous system, mainly affect the "white matter" of the cerebrum and cerebellum, and are therefore generally known as inherited white matter disorders. A wide variety of disorders occur: connatal cerebral white matter hypoplasias such as Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, Canavan disease, Alexander disease, and metachromatic leukodystrophy; lysosomal storage diseases such as Krabbe disease; peroxisomal diseases such as adrenoleukodystrophy; amino acid metabolism disorders such as phenylketonuria and maple syrup urine disease; folic acid metabolism disorders such as homocystinuria, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency, and methionine adenosyl transferase deficiency; Lowe syndrome (Golgi transport system disorders), giant axonal neuropathy (abnormal intermediate filament structure), and merosin-deficient congenital muscular dystrophy (abnormal glycosylation); and conditions due to drugs or infection.
This website has been produced by the team working on the "Development of Systems for the Diagnosis, Treatment, and Study of Inherited White Matter Disorders" as part of the Research Study Team for Intractable Diseases, funded by a Health Labour Sciences Research Grant, with the aim of contributing to the diagnosis and treatment of these conditions (Hitoshi OSAKA, Department of Pediatrics, Jichi Medical University).